The management of the obsolescence has as main scope that one to guarantee a support to the system cost-effective during its entire cycle of life: the aim, in fact, is that one to define a trade-off between the several requirements and to supply a process of effective management.
They would have to be defined, therefore, those actions to put in existence to the aim to prevent or to resolve the effects which had to the DMSMS problems.
In riassuntiva way, I can say that, typically, the main problems to hold in consideration and to analyze in a Obsolescence Management Plan (OMP) sono1:
- To consider all the materials in use, without to attend to the fact that can be members inside develops you for a specific plan of the company (Make) or COTS;
- To pursue the minor life cicle cost for the supported system, holding in debita consideration its performances, its availability and its manutenibilitÓ;
- To be compatible with the actions of support already the eventual ones constraint of the situation implemented and;
- Sturdy and flexible being in an atmosphere characterized from continuous changes.
In the light of this, therefore, the management of the obsolescences would have to be considered like an element of the widest management of the risks of a plan.
Being based on the experience and the analysis, moreover, the Project Manager would have to hold in consideration also the being followed aspects of the issue:
- Which it would be the impact on the performances of the system because of one lack of by now obsolete replacement parts;
- Which it would be the probable cost of a premature substitution of by now obsolete parts or that one of other actions in order to go around the problem;
- Which effectively it is the manifest probability that the obsolescence.
In order to analyze these last aspects of the problem in synthetic way, it is often made resorted to a graphical aid that puts in relation the three variable ones and allows one total vision of the situation.
In the successive figure it comes, exactly, shown the system with which the schematizzazione of the three aspects is tried to consider.
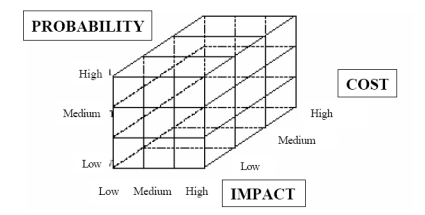
Figure 4.1: Outline for the classification of the problem obsolescences.
As it is looked at, to every face of the cube a risk element corresponds to consider:
- The Impact of the obsolescence on the system;
- The Cost of the possible resolution;
- The Probability with which the obsolescence will be taken place.
For everyone of these factors three levels of occurrence are considered:
- Low (Low);
- Mean (Medium);
- High (Hight).
Therefore, based on the result of this analysis on the three main factors of risk, the Project Manager decides the strategy to pursue.
In last analysis, the managerial process for the problem of the obsolescences can be outlined, in general terms, in the following steps.
- Identification/Verification, to second of the approach that is decided to follow, of the obsolete part (for clarifications on the approach to the Par.4.1 problem);
- To analyze of the impact on the system;
- To analyze of the impact on the logistics;
- To identify solutions alternatives;
- To identify eventual supplyes available near retailers or suppliers;
- To identify ingegneristiche solutions;
- To estimate the solutions alternatives;
- To give one priority to the solutions and schedularle in the time;
- To find the deep ones in order to realize the solutions and to implement them effectively.
- 1: Defence Standard 00-71, Issue 2: Obsolescence Management, The Ministery of Defence, Directorate of Standardization, 27 January 2001.

